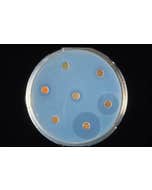
Kit to measure the effectiveness of 4 antibiotics on 2 strains of bacteria
Topics covered:
- Learning to work in a sterile condition in a microbiology laboratory
- Performing an antibiogram using the agar diffusion method
- Determining the minimum inhibitory concentration of the antibiotic (MIC)
- Illustrating the concept of bacterial genetic variation
Principle and objective:
Measuring the effectiveness of 4 antibiotics on 2 bacterial strains. After a quick reactivation of lyophilized strains, each pair seeds the two bacterial strains on two separate agar plates. 4 different antibiotic disks are then placed. The results are read after 24 to 48 hours. Bacterial growth inhibition is indicated by a 'clear' circular zone without bacteria, the zone being wider the more sensitive the bacteria is to the antibiotic.
The experiment lasts 60 minutes (incubation 24h to 48h). Reagents are provided for 25 experiments.
Composition:
2 tubes of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis inoculum, lyophilized dense culture (Pasteur strain), 2 sterile water tubes, antibiotics (4 x 50 disks) ampicillin 10 µg, penicillin 10 µg, tetracycline 30 µg, nalidixic acid 30 µg, Mueller-Hinton medium in ready-to-pour bottle (5 x 200 ml), 50 Petri dishes 90 mm 3 prongs, 50 Pasteur pipettes 1 ml, 50 sterile spreaders.
Comments:
Our instructions guide you through the experimental protocol. The strains are considered as inoculums. Petri dishes of 90 mm should be used to prevent crossing of inhibition circles. All consumables are available on Jeulin.com.
| Thématique TP | Biologie |